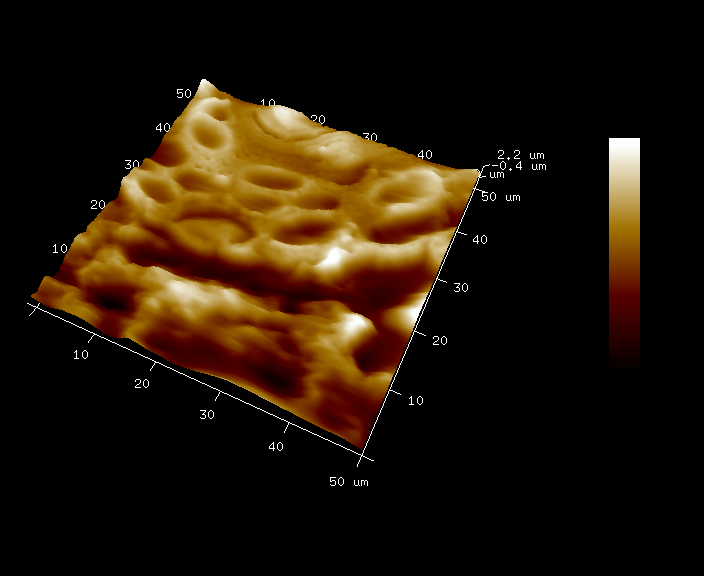
Desquamation
May 2022
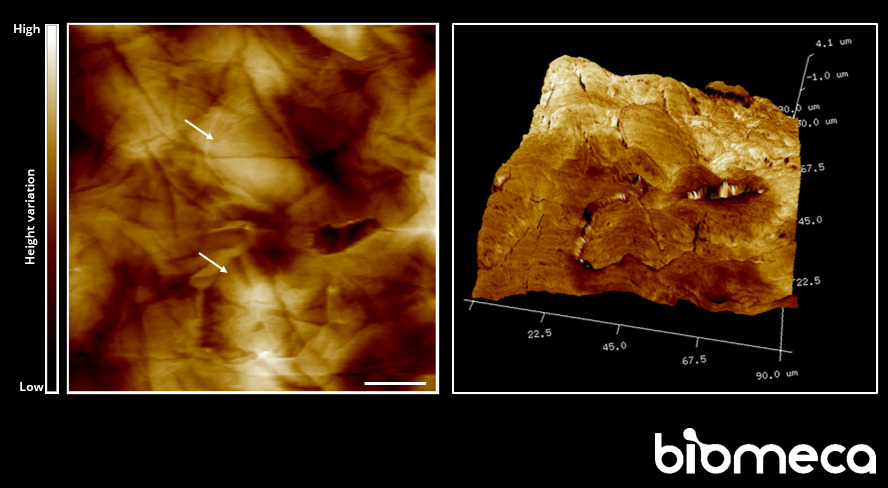
Skin explant topography performed by high-resolution AFM imaging. Some corneocytes involved in the desquamation process are visible (arrows).
Scale bar: 20µm.
Regeneration
April 2022
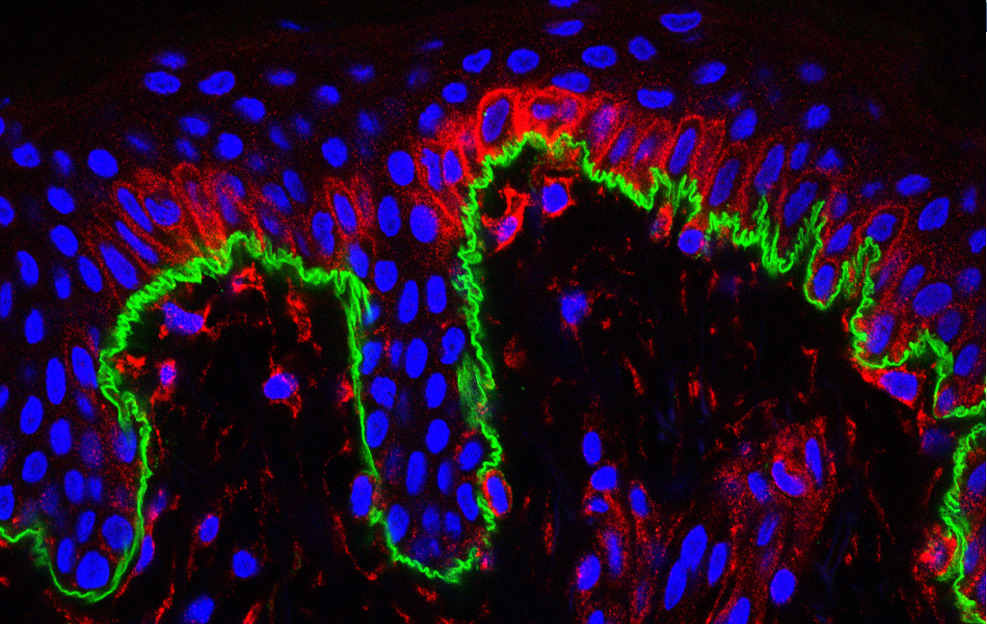
Coupling Atomic Force Microscopy and confocal microscopy to showcase skin regeneration
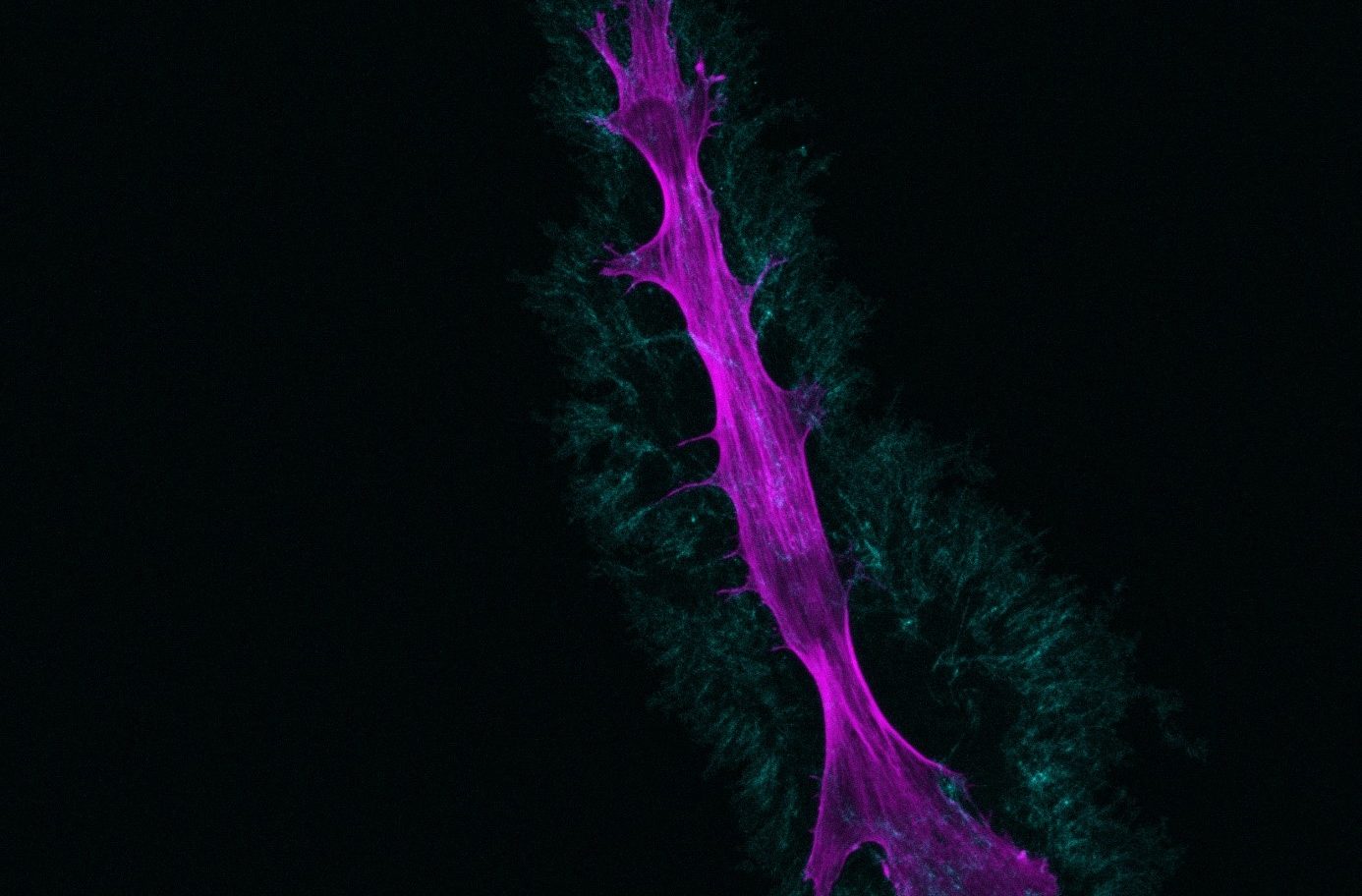
Fibroblasts
September 2021
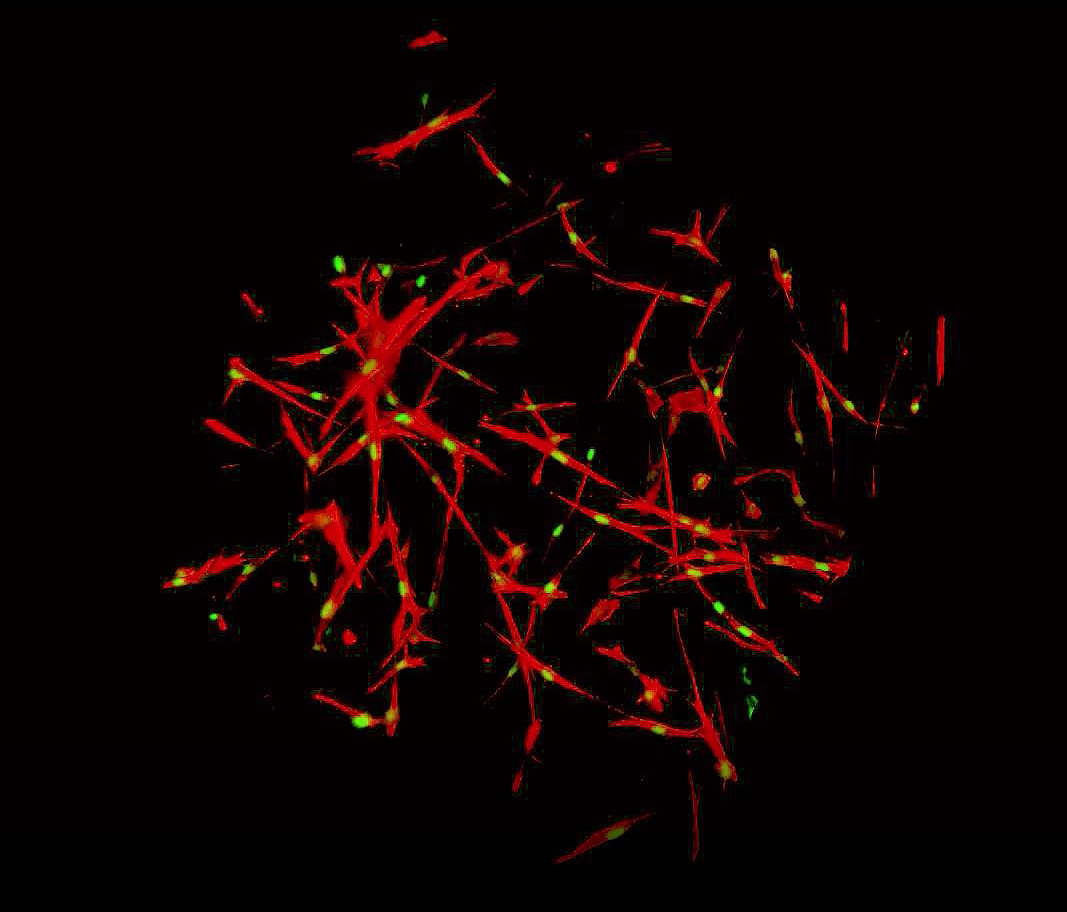
Culture of fibroblasts in collagen discs, allowing the culture of fibroblasts in a three dimensional system, alternative to the classical two dimensional culture system.
Nuclear (green) and actin cytoskeleton (red) labeling.
Dermal-epidermal junction
June 2021
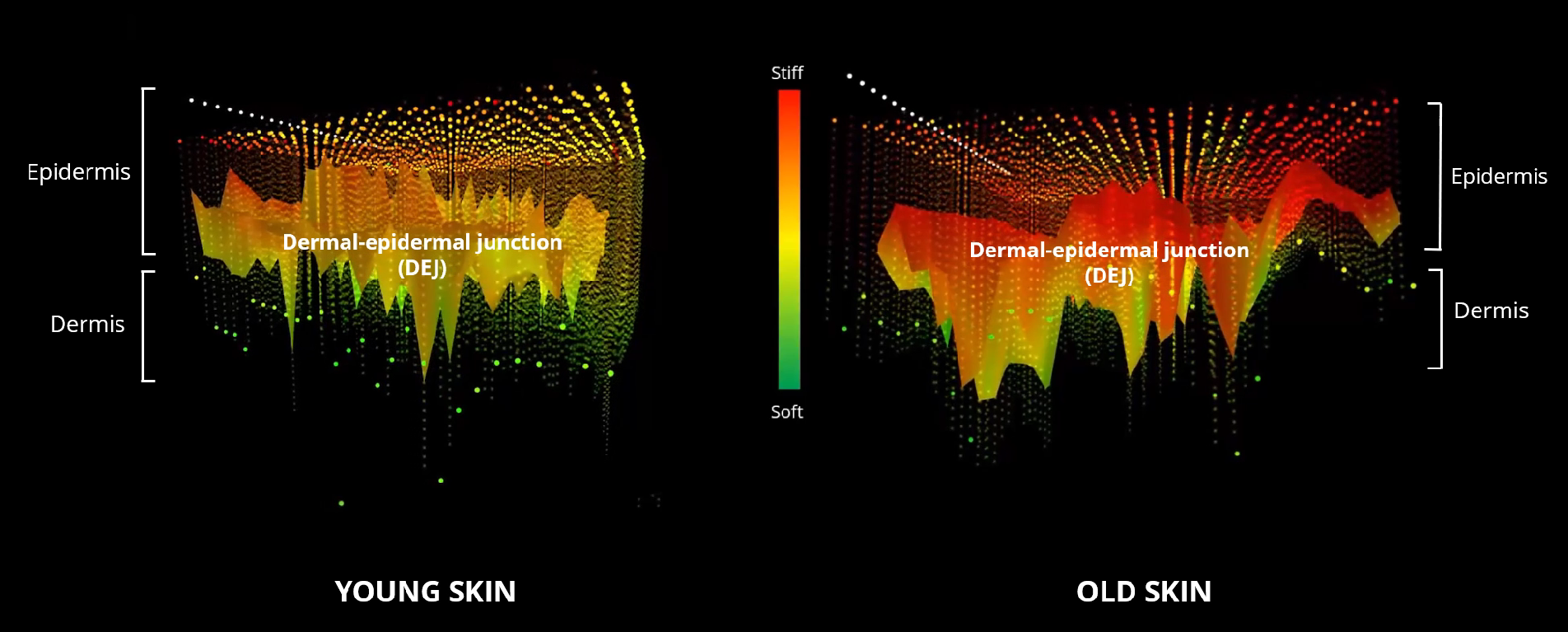
3D force map of dermal-epidermal junction (DEJ) evolution over time with Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM).
Each pixel corresponds to a stiffness value:
🟢 indicates a low stiffness
🔴 indicates a high stiffness
🟠 indicates an intermediate value
A new solution to assess skin ageing focusing on DEJ.
Skin compartments
February 2021
AFM topographic image of skin from abdominoplasty, highlighting the main skin compartments:
👉 At the top of the picture, epidermis with its 3 layers (granulosa, spinous and basal) and at the very top, stratum corneum.
👉 Dermis, at the bottom of the picture, with above epidermis-dermis junction-containing area.
Fibroblasts
November 2020
High-resolution image of a fibroblast using confocal microscopy (for phalloidin labeling of actin) and second harmonic microscopy (for collagen).
Carried out on an uncoated petri dish, with a collagen neo-synthesised by fibroblast.
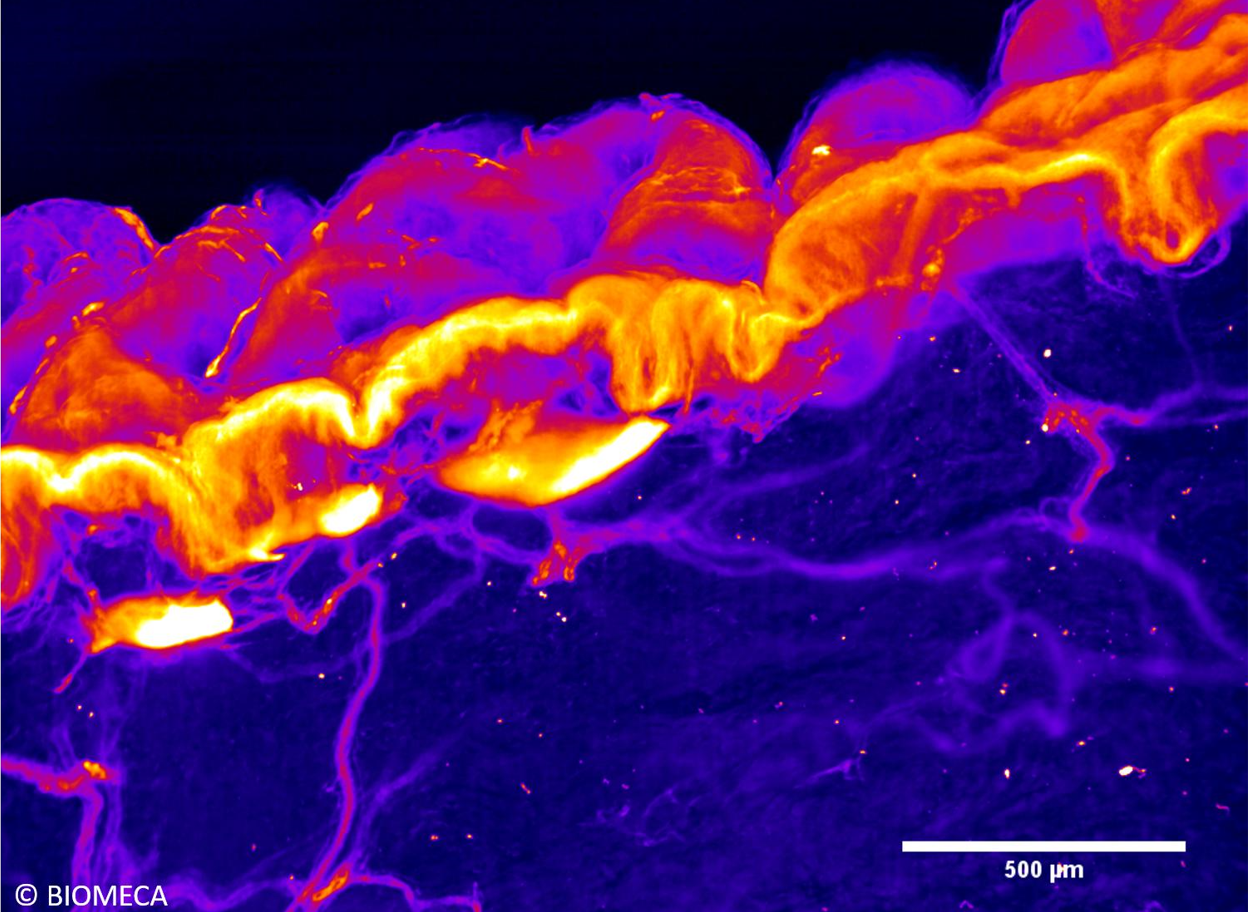
Skin aging process
July 2020
Microcirculation study through skin capillaries high resolution imaging by light sheet fluorescence microscopy in order to better understand skin aging process.